
In today's digital world, originality is essential for students, educators, and professionals. The risks of unintentional plagiarism can jeopardize academic reputations and professional integrity.
Understanding what is plagiarism checking is crucial for anyone creating or evaluating content. With advanced technology, it is easier than ever to ensure that your work is both authentic and properly credited.
This guide will explain what plagiarism is, how checking tools work, and the best ways to use them in 2026. You will discover practical steps, real-world examples, and the latest trends in plagiarism detection.
Whether you are a student, teacher, or business professional, mastering plagiarism checking helps you protect your work and maintain trust. Take the first step toward academic honesty and digital integrity with this comprehensive resource.
What Is Plagiarism ?

Plagiarism is a term everyone hears, yet its full meaning often goes misunderstood. At its core, plagiarism is presenting someone else's work, ideas, or words as your own, without proper acknowledgment.
Unintentional plagiarism happens when someone fails to cite sources properly or misunderstands how to paraphrase. In both cases, what is plagiarism checking becomes a safeguard, helping individuals catch errors before submission.
Types of Plagiarism
Several forms of plagiarism exist, each with unique characteristics:
Direct plagiarism: Copying text word-for-word without credit.
Mosaic plagiarism: Piecing together phrases from various sources without proper citation.
Self-plagiarism: Reusing your own previous work without disclosure.
Accidental plagiarism: Failing to cite sources due to lack of knowledge or oversight.
For example, copy-pasting paragraphs from a website, paraphrasing ideas without attribution, or submitting the same essay for multiple classes all constitute plagiarism. What is plagiarism checking is crucial in identifying these issues early.
Where Plagiarism Occurs
Plagiarism is not limited to academic settings. It appears in professional reports, creative works, and scientific publications. Students, educators, writers, and business professionals all encounter the risks associated with plagiarism. In every context, what is plagiarism checking provides a layer of protection against both accidental and deliberate mistakes.
What Is Plagiarism Checking?
Plagiarism checking is the process of identifying whether a piece of content contains text, ideas, or structures that are copied or too closely resemble existing sources without proper attribution.
The process begins when a user submits text, which the checker scans for similarities using various algorithms.
These algorithms include:
String matching: Detects exact copies of text sequences.
Fingerprinting: Breaks content into unique patterns for comparison.
Stylometry: Analyzes writing style and linguistic markers.
Semantic analysis: Understands context and meaning, not just word-for-word matches.
Machine learning and AI now enable what is plagiarism checking to identify paraphrased or reworded content, making detection more accurate. However, limitations exist. False positives may occur, such as flagged citations or common phrases. False negatives can happen if the source is not in the database or in another language.
For example, Turnitin uses a massive repository and generates a similarity index, showing the percentage of matched text. It’s important to distinguish between similarity and plagiarism. Not all matches are problematic; properly cited quotes or references often appear in similarity reports but do not constitute plagiarism.
By understanding these technical aspects, users can better interpret what is plagiarism checking results and avoid common pitfalls.
In simple terms
It answers the question:
👉 “Is this content original, or does it borrow from someone else without credit?”
Major Plagiarism Checking Tools in 2025
The market for what is plagiarism checking tools is broad, with options tailored for educators, students, publishers, and businesses. Leading solutions include Turnitin, Grammarly, Unicheck, Copyscape, and Scribbr. Each offers unique features, such as database size, level of report detail, and integration with learning management systems.
Below is a comparison of key features:
Tool | Database Size | Report Detail | Integrations | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Turnitin | Extensive | High | LMS, APIs | AI writing detection |
Grammarly | Large | Moderate | Browsers, MS | Real-time feedback |
Unicheck | Wide | Detailed | LMS | Code, image analysis |
Copyscape | Web-focused | Basic | Web | Website plagiarism |
Scribbr | Academic | In-depth | Standalone | Citation checking |
Free tools offer basic checks but may lack depth and accuracy. Paid solutions provide more comprehensive analysis, support, and privacy controls.
Recent advancements now allow what is plagiarism checking to extend beyond text. Some tools can detect copied images or even programming code, making them valuable for creative and technical fields. The choice of tool depends on the user’s needs, desired accuracy, and budget.
Selecting the right solution ensures that what is plagiarism checking aligns with academic, professional, or publishing standards.
Detector AI: Integrated AI and Plagiarism Detection
Detector AI represents the next generation of what is plagiarism checking. This platform combines AI-generated content detection with advanced plagiarism analysis, offering a dual-layered approach to authenticity.
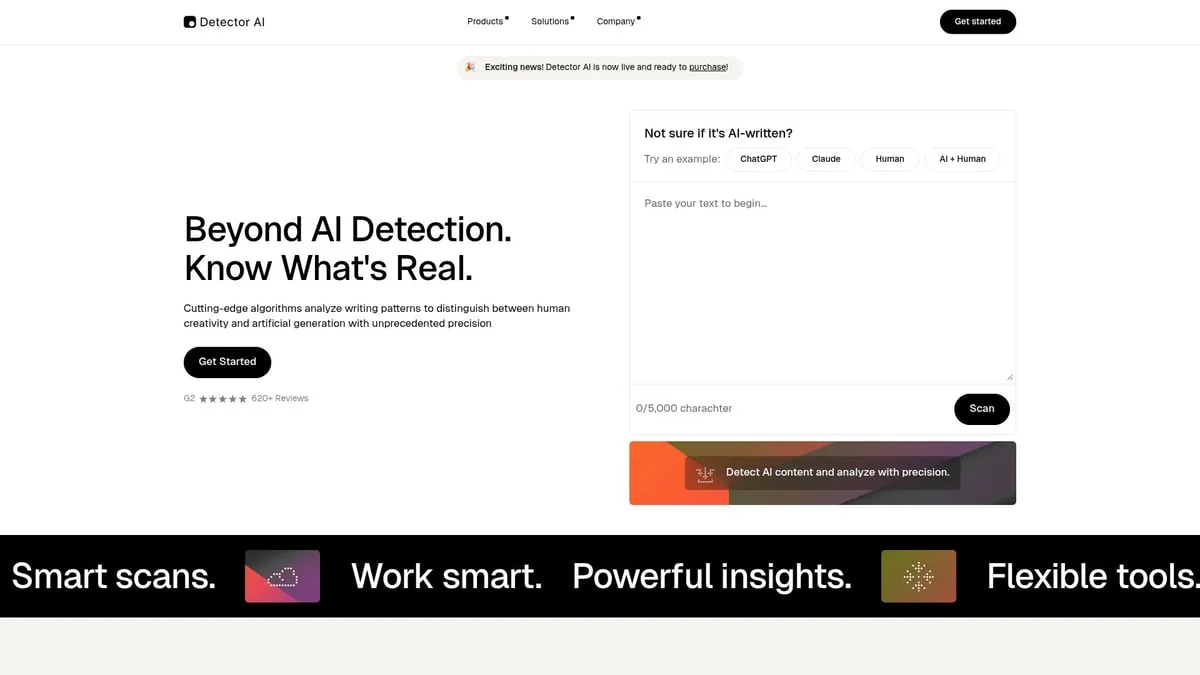
Detector AI examines writing patterns, sentence structure, and linguistic fingerprints, comparing them to both public and proprietary sources. This enables sentence-level analysis and precise source matching.
Benefits include:
Detailed feedback for educators, editors, and professionals
Clear identification of both AI-generated and plagiarized content
Comprehensive reporting to support revisions and transparency
Use cases for Detector AI range from verifying student assignments to editorial review and validating professional documents. By integrating AI detection with traditional plagiarism checking, Detector AI provides a robust solution for modern content evaluation needs.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use a Plagiarism Checker in 2026
Using a plagiarism checker effectively is an essential skill for anyone who values originality and academic integrity. This step-by-step guide will walk you through exactly what is plagiarism checking, from preparing your document to revising your work based on the report. By following these modern best practices, you can ensure your writing remains authentic and properly credited.

Preparing Your Document
Before you begin the process of what is plagiarism checking, it is important to ensure your document is ready for analysis. Start by saving your work in an accepted file format. Most tools in 2025 support PDF, DOCX, and TXT files. This helps prevent formatting errors during the upload.
Remove any personal details or metadata from your file. Many checkers automatically anonymize submissions, but it is best to double check. Properly cite all your sources and references before running a check. This step reduces unnecessary flags for missing attributions.
If you have used AI-generated content in your writing, highlight or mark these sections. Some plagiarism tools now offer features to identify and differentiate AI-generated text. Taking these steps helps the checker provide a more accurate assessment of originality.
Submitting Your Work to a Plagiarism Checker
Once your document is prepared, the next step in what is plagiarism checking is submitting your work to the tool of your choice. Begin by selecting a reputable plagiarism checker that suits your needs. Some platforms require you to create an account, while others allow guest submissions.
You can typically upload your document directly or copy and paste your text into the checker. Decide whether you want your document stored permanently in the tool's database or checked temporarily. Permanent storage helps prevent future duplication, while temporary checks prioritize privacy.
Always review the tool's privacy and data storage policies before submitting sensitive content. Leading solutions, such as those detailed in the Plagiarism Checker Tool Overview, ensure robust security and transparency in handling your files. Making an informed choice at this stage is a key aspect of responsible what is plagiarism checking.
Analyzing the Plagiarism Report
After submission, the tool generates a detailed report. Understanding this report is central to what is plagiarism checking. Most checkers display a similarity percentage, indicating how much of your content matches existing sources.
Carefully review the highlighted sections. These often include direct quotes, paraphrased passages, and areas lacking citations. Not all matches mean plagiarism; common phrases and properly cited material might also appear. Differentiate between genuine concerns and false positives, such as standard references or universally used expressions.
A typical report provides links to matched sources, making it easier to verify flagged content. Use this information to assess whether your citations are correct and complete. For example, a properly cited quote should not be considered plagiarism, while a paraphrased idea without credit may require revision.
Some advanced tools offer sentence-level analysis, helping you see precisely where originality issues occur. This granular feedback empowers you to refine your work and better understand what is plagiarism checking in practice.
Taking Action: Revising and Resubmitting
When your report reveals problematic areas, take immediate steps to address them. The final stage of what is plagiarism checking involves revising your document for authenticity and accuracy. Start by paraphrasing flagged sections in your own words, or add quotations and citations where necessary.
Use the report's feedback as a learning tool to strengthen your writing. If you are unsure about a flagged passage, consult your instructor or an editor for guidance. Collaboration at this stage supports your growth as a responsible writer.
After making revisions, resubmit your document to the plagiarism checker. Compare the new report with the previous one to confirm improvements. This iterative process reinforces the importance of thorough what is plagiarism checking and helps you build habits for original, well-cited work.
Best Practices for Avoiding Plagiarism
Maintaining originality is essential in any academic or professional setting. By following best practices for avoiding plagiarism, you can confidently answer what is plagiarism checking and ensure your work meets the highest standards of integrity and authenticity.

Effective Paraphrasing and Quoting
One of the most important skills in maintaining academic honesty is learning how to paraphrase and quote correctly. When you paraphrase, you must rewrite ideas in your own words and sentence structure, rather than just swapping out a few terms. This helps you avoid direct copying and demonstrates your understanding.
Good paraphrasing example:
Original: "Plagiarism checking tools compare submitted text to a vast database." Paraphrased: "Tools designed to detect plagiarism scan your writing against extensive repositories of content."
Bad paraphrasing example:
"Plagiarism checking tools check your text with a huge database."
Notice how the good example rewords and restructures the idea, while the bad example is too similar to the original.
Use direct quotes sparingly and always enclose them in quotation marks, followed by a citation. If you are unsure, tools like Grammarly or Turnitin can help review your paraphrasing quality.
By mastering these techniques, you not only avoid plagiarism but also gain a deeper understanding of what is plagiarism checking and how it safeguards your academic journey.
Proper Citation and Referencing
Citing your sources accurately is critical for maintaining credibility and answering what is plagiarism checking in practice. Different citation styles, such as APA, MLA, and Chicago, have specific rules for referencing books, articles, and web pages.
Common citation mistakes include:
Forgetting page numbers for direct quotes
Mixing up citation styles in one document
Not including all sources in the bibliography
Consider using reference management tools like Zotero, EndNote, or Mendeley to organize your sources and generate citations automatically.
Citation examples:
Always double-check your references before submission. Proper citation ensures transparency and aligns with the principles behind what is plagiarism checking.
Academic Integrity Policies and Education
Academic institutions enforce integrity through honor codes and strict policies. Students and staff are often required to complete training on plagiarism awareness and responsible research.
Many universities offer workshops, online modules, and resources to promote ethical writing practices. Plagiarism checkers play a key role in supporting these efforts by providing objective feedback.
For tailored guidance on maintaining academic honesty and making the most of plagiarism detection tools, students can consult Academic Integrity for Students.
Understanding institutional expectations is vital for anyone asking what is plagiarism checking and striving to uphold these standards.
Self-Checking and Peer Review
Running a self-check with a plagiarism tool before you submit your work is a proactive way to catch unintentional mistakes. Peer review also helps, as classmates or colleagues can spot overlooked issues and suggest improvements.
Set up peer-review protocols by:
Sharing drafts in trusted groups
Using plagiarism reports as a discussion tool
Giving constructive feedback on citations and paraphrasing
These steps reinforce your understanding of what is plagiarism checking and empower you to submit work with confidence.
Interpreting Plagiarism Reports: What Educators and Students Need to Know
Understanding what is plagiarism checking is essential for both students and educators, especially when interpreting detailed plagiarism reports. These reports are more than just numbers; they require careful analysis to determine what the results truly mean.
Making Sense of Similarity Scores
When you receive a plagiarism report, the similarity score is often the first thing you notice. This percentage reflects how much of your text matches sources in the tool’s database. However, what is plagiarism checking in practice? It is not simply about the number; it is about understanding what those matches represent.
Similarity Percentage | Typical Meaning | Action Needed |
|---|---|---|
0–10% | Likely common phrases or citations | Usually acceptable |
11–25% | Some overlap, check sources | Review for proper citation |
26–50% | Significant overlap, possible issues | Investigate further |
51%+ | High risk, likely problematic | Immediate review required |
Always look beyond the score to see if the matches are direct quotes, properly cited, or accidental overlaps.
Context: Not All Matches Are Equal
Context plays a crucial role in interpreting what is plagiarism checking and its outcomes. For example, a high similarity score may result from using common terminology, referencing widely used sources, or including a bibliography. These are not necessarily signs of misconduct.
Case studies show that students often get flagged due to proper citations or shared assignment prompts. Educators need to distinguish between legitimate overlap and actual plagiarism. Reviewing each highlighted section helps separate harmless matches from true issues.
What Happens After a Flag?
Once content is flagged, what is plagiarism checking protocol? Educators typically:
Review the report alongside the original sources.
Identify whether flagged content is properly cited or paraphrased.
Decide if the similarity is justified or if it requires revision.
Students have the right to:
Request clarification about flagged sections.
Provide explanations for overlaps.
Contest results if they believe the report is inaccurate.
This process encourages dialogue and helps maintain fairness.
Transparency and Acceptable Thresholds
Transparency in sharing reports is vital for trust. Institutions often set acceptable similarity thresholds, commonly under 15 percent. However, these numbers are guidelines, not rules. For example, Turnitin reports can include false positives, especially from cited material or standard phrases.
For further insights into interpreting plagiarism reports and best practices, you can explore the Plagiarism Detection Blog Insights.
Clear communication of what is plagiarism checking results ensures that both educators and students understand the implications and can act appropriately.
Resources and Further Reading
Navigating the landscape of what is plagiarism checking requires reliable, up-to-date resources. Whether you are a student, educator, or professional, having access to trusted tools, guides, and organizations is essential for maintaining academic integrity and understanding best practices.
Top Plagiarism Checking Tools
To understand what is plagiarism checking, it is helpful to explore the leading platforms available in 2025. Each tool offers unique features, database coverage, and reporting styles.
Tool | Website | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
Turnitin | turnitin.com | Academic focus, robust database, detailed reports |
Grammarly | grammarly.com | Integrated writing and plagiarism checks |
Unicheck | unicheck.com | Real-time detection, cloud integration |
Copyscape | copyscape.com | Web content protection, batch scanning |
Scribbr | scribbr.com | Student-friendly, citation help |
For an in-depth look at the current state of detection technologies and industry data, the Plagiarism Detection Market Report provides valuable insights into tool adoption and trends.
Citation Guides and Reference Management
Mastering citation is a crucial part of what is plagiarism checking. Here are essential guides and tools:
APA, MLA, Chicago Style Manuals: Official style guides for formatting and citing sources.
Purdue OWL: Comprehensive online resource for all major citation styles.
Reference Management Tools: Zotero, EndNote, and Mendeley streamline citation and bibliography creation.
Academic Integrity Resources
Understanding what is plagiarism checking goes hand in hand with promoting academic honesty. Explore these organizations for policy guidance and support:
International Center for Academic Integrity: Resources on developing and maintaining integrity policies.
plagiarism.org: Educational articles, FAQs, and best practices for students and teachers.
Tutorials, Video Guides, and Further Reading
Building skills in avoiding plagiarism is an ongoing process. The following resources offer practical help:
University writing centers often provide video tutorials on using plagiarism checkers and proper citation.
Academic libraries frequently host workshops on ethics and the responsible use of sources.
For a look at changing student perspectives, read Student Attitudes Toward Plagiarism, which explores how young people view originality in the digital age.
Books and Articles on Academic Honesty
"Doing Honest Work in College" by Charles Lipson
"The Little Book of Plagiarism" by Richard A. Posner
Peer-reviewed articles from journals on education and ethics
FAQs and Support Contacts
If you still have questions about what is plagiarism checking, consult your institution’s academic support office or writing center. Many universities offer confidential consultations and workshops tailored to your needs.
Check official FAQs on trusted sites like plagiarism.org, or reach out to support teams of the major plagiarism checking platforms for technical assistance.
By leveraging these resources, you can confidently navigate the complexities of what is plagiarism checking and uphold the highest standards of academic and professional integrity.



